Radiation tolerant lights
This document was created to assist anyone who needs lights for nuclear applications. Today all nuclear customers are opting for new radiation tolerant LED lights. Old lighting technologies such as halogen bulbs, metal halide, and sodium lights are still in use in many nuclear plants, but these are gradually being upgraded to LED lights. The two main reasons for changing to LED lights are:
-increased light output
-minimal maintenance
Common questions when choosing new lights:
-Is the light for use underwater or in air?
-What is the radiation level where the light is going to be placed?
-How to power the light?
-How many lights are needed in the reactor and fuel pools?



-Is the light for use underwater or in air?
A vital question to be answered is if the light is going to be used underwater or in air. This may seem easily answered, but during an outage, the water level changes and could fall below the level of a light that was accidentally left powered on. For this reason, overheating protection is incorporated into every light unit to prevent damage.
Users with experience of halogen lights know that the heat produced in the bulb can melt the material around it. Although the heat production in a LED light is less, it is enough to be an important factor when designing the light. Stainless steel is a suitable material for underwater lights where the heat is transferred to the surrounding water. For lights in air, such as ones used in CCTV applications, cooling fins of suitable material are needed which also allows for the footprint to remain as small as possible.
Solely relying on overhead lights to illuminate a pool filled with water is generally not sufficient because some of the light is reflected at the water surface. Therefore, proper underwater lights are recommended to view equipment placed in nuclear pools.
Our underwater lights for nuclear plants are pressure tested for use down to 50 m (165 ft) underwater. Few pools in nuclear sites are deeper than 35 m (115 ft). Lights made for air installation are not waterproof but generally provide IP65 or IP67 protection from water jets or extremely humid environments.
-What is the radiation level where the light is going to be placed?
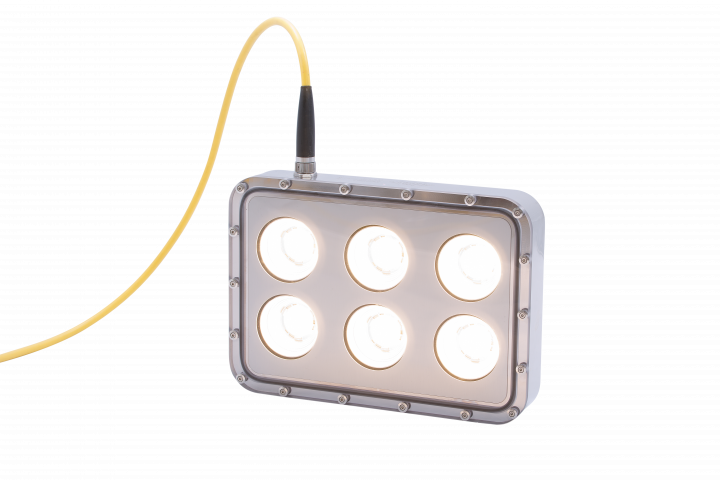
Lights that are going to be mounted underwater in a nuclear facility typically require radiation resistance. Permanent pool lights are commonly placed just below the water surface and are far away from the radiating nuclear fuel. However, since they are permanently installed, the accumulated dose is going to be considerable over time. Ahl-Light 70 https://www.ahlbergcameras.com/products/lights/ahl-light-70/ is an example of permanent pool lighting with a robust radiation tolerance.
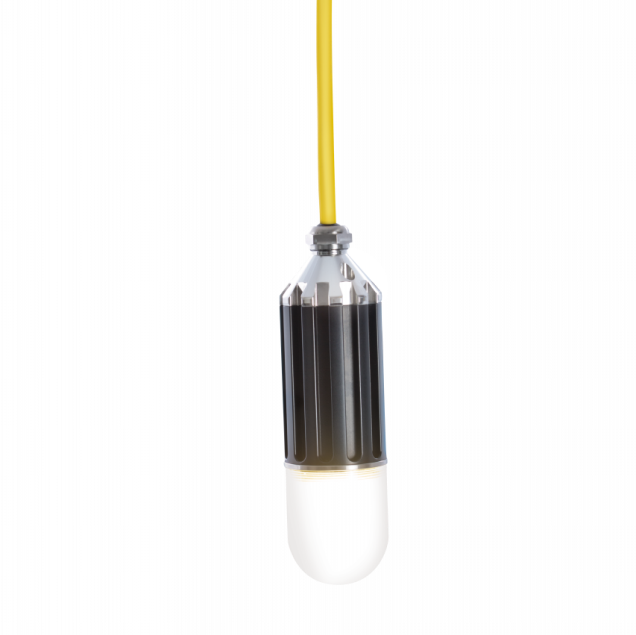
Lights that are used during work campaigns in nuclear ponds are exposed to higher radiation during shorter periods. Our radiation tolerant lights have a life expectancy of greater than 50,000 hours. This eliminates the need to frequently replace other non-radiation tolerant lights.

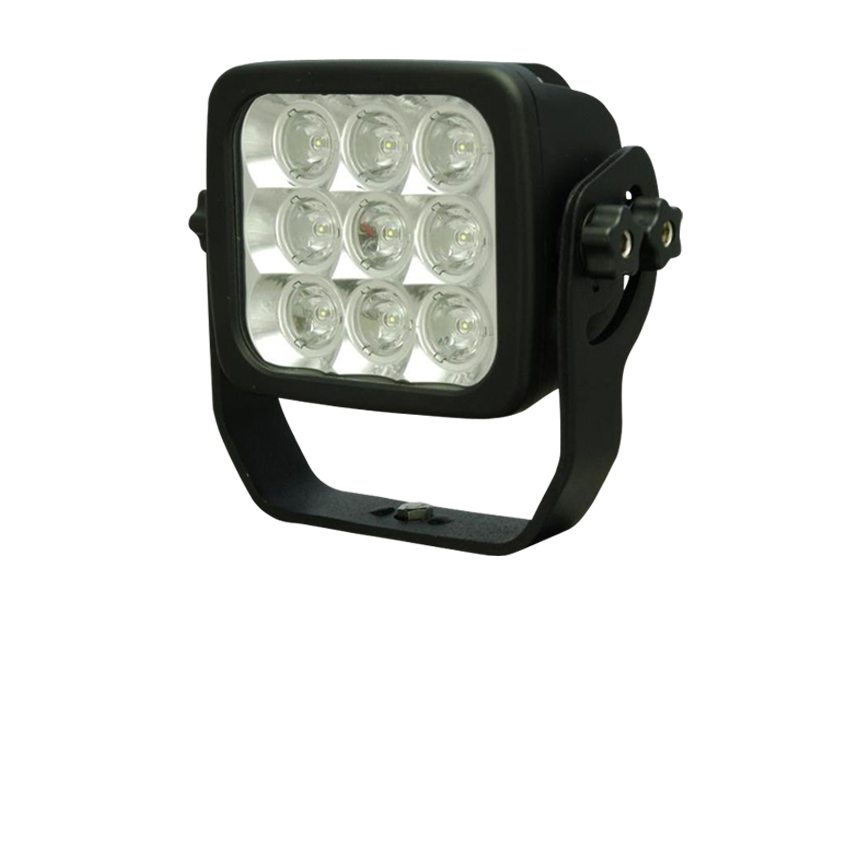
Air lights that are mounted in rooms where plant personnel can access during operation can be of different standard types. But, for lights that are used in areas where radiation tolerant cameras are placed, it is necessary for those lights to be radiation tolerant. Ahlberg’s CCTV LED 5 light https://www.ahlbergcameras.com/products/lights/cctv-led-5/ can be used in highly irradiated areas such as nuclear power plant containments and hot cells.
-How to power the light?
Lights can become radiation tolerant by different means. Separating the system into one lighting unit and one power supply unit is a method used by Ahlberg Cameras. By separating these units, the power supply unit must be placed between the light and power outlet. The power supply unit can be placed anywhere there is a power outlet or a central power arrangement.
CCTV lights are powered by the same unit that powers and controls the camera.
https://www.ahlbergcameras.com/products/lights/
-How many modern lights are needed in the reactor and fuel pools?
Going from older light technologies to modern LED lights can reduce the number of lights by half in BWR and PWR pools. To avoid shade behind objects placed in the pool, installing lights on each side of the pool is optimal.